The Importance of Earthquake Foundation Retrofits
Foundation earthquake retrofitting represents a crucial intervention for enhancing the resilience of homes against the forces unleashed during seismic events. This practice involves the strengthening of a building’s structure to significantly reduce the risk of earthquake damage. Particularly in areas prone to seismic activity, the question of whether to invest in earthquake retrofitting is not only about safeguarding a property but also about ensuring the safety of its occupants. Through an examination of the various aspects of retrofitting, from its fundamental principles to cost considerations and beyond, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview that illuminates the value and necessity of retrofit work in earthquake-vulnerable zones.
Table of Contents
What is Earthquake Retrofitting and Why is it Necessary?
Understanding the Basics of Retrofit and Earthquake Resistance
At its core, earthquake retrofit involves modifying existing structures to enhance their ability to withstand the seismic forces they were not originally designed to endure. This process can include the strengthening of the building’s frame and the foundation to prevent catastrophic failure during an earthquake. Retrofitting is particularly vital for older homes, many of which lack the seismic resistance features integrated into modern building codes. Such interventions are essential not only for safeguarding the physical structure of a house but also for protecting the lives of its inhabitants against earthquake shaking and damage.
Typically, retrofit strategies may involve the installation of bolt retrofit systems or the application of brace-and-bolt retrofits. These methods aim to fortify the connection between the house’s structure and its foundation, which is critical in preventing the building from sliding off its base in the event of major earthquake shaking. By strengthening these critical points, retrofitting acts as a vital buffer against the forces of nature, significantly lowering the risk of severe earthquake damage.
The Critical Role of Seismic Retrofit in Earthquake Safety
Earthquake-induced damage can range from minor cracks in the walls to the complete collapse of buildings, depending on the magnitude of the earthquake and the resilience of the structure. Seismic retrofit plays an indispensable role in improving a building’s earthquake resistance, thereby significantly reducing the potential for property loss and, more importantly, saving lives. The importance of seismic retrofit, especially in earthquake-prone areas, cannot be overstated. Implementing retrofit solutions not only makes homes safer but also contributes to the overall disaster preparedness of a community.
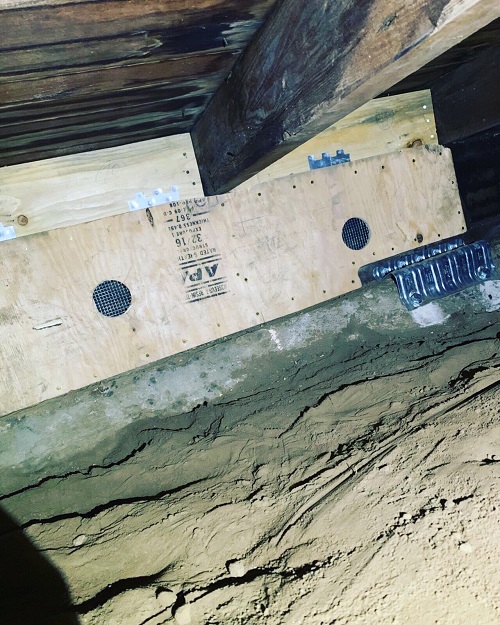
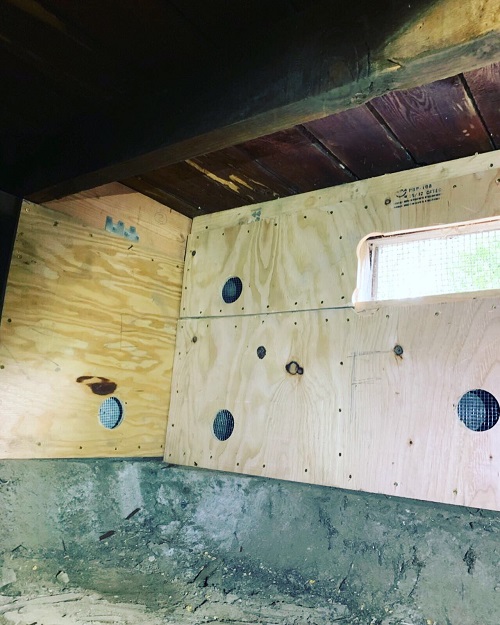
Seismic retrofitting involves various techniques and technologies designed to enhance the structural integrity of buildings. This could include the strengthening of cripple walls with plywood to make them less susceptible to collapse, the addition of anchor bolts in the foundation to secure the house to its concrete base more robustly, and the installation of framing anchors to improve the overall stability of the structure. Such comprehensive retrofit measures ensure that homes are better equipped to face the rigors of earthquake shaking, ultimately leading to a more resilient built environment.
Differentiating Between Bolt Retrofit and Brace-and-Bolt Retrofit
Bolt retrofit and brace-and-bolt retrofit are two principal methods employed to enhance earthquake resistance in existing structures. Bolt retrofit focuses on anchoring the house more securely to its foundation using bolts, thereby significantly reducing the likelihood of the structure moving independently of its base during an earthquake. This method is particularly effective for homes with a raised foundation, where there is a clear gap between the house frame and the foundation itself.
On the other hand, brace-and-bolt retrofit entails the addition of bracing to the cripple walls and bolting the house to its foundation. The bracing usually consists of wood or steel panels that are installed on the interior or exterior of the cripple wall sections to prevent lateral movement during seismic activity. When combined, bracing and bolting provide a comprehensive seismic strengthening solution, ensuring that the house is both rigid and securely anchored to its base. This type of retrofit is highly recommended for homes in seismically active regions as it addresses both vertical and horizontal forces exerted during an earthquake.



What is Earthquake Retrofitting and Why is it Necessary?
Understanding the Basics of Retrofit and Earthquake Resistance
At its core, earthquake retrofit involves modifying existing structures to enhance their ability to withstand the seismic forces they were not originally designed to endure. This process can include the strengthening of the building’s frame and the foundation to prevent catastrophic failure during an earthquake. Retrofitting is particularly vital for older homes, many of which lack the seismic resistance features integrated into modern building codes. Such interventions are essential not only for safeguarding the physical structure of a house but also for protecting the lives of its inhabitants against earthquake shaking and damage.
Typically, retrofit strategies may involve the installation of bolt retrofit systems or the application of brace-and-bolt retrofits. These methods aim to fortify the connection between the house’s structure and its foundation, which is critical in preventing the building from sliding off its base in the event of major earthquake shaking. By strengthening these critical points, retrofitting acts as a vital buffer against the forces of nature, significantly lowering the risk of severe earthquake damage.
The Critical Role of Seismic Retrofit in Earthquake Safety
Earthquake-induced damage can range from minor cracks in the walls to the complete collapse of buildings, depending on the magnitude of the earthquake and the resilience of the structure. Seismic retrofit plays an indispensable role in improving a building’s earthquake resistance, thereby significantly reducing the potential for property loss and, more importantly, saving lives. The importance of seismic retrofit, especially in earthquake-prone areas, cannot be overstated. Implementing retrofit solutions not only makes homes safer but also contributes to the overall disaster preparedness of a community.
Seismic retrofitting involves various techniques and technologies designed to enhance the structural integrity of buildings. This could include the strengthening of cripple walls with plywood to make them less susceptible to collapse, the addition of anchor bolts in the foundation to secure the house to its concrete base more robustly, and the installation of framing anchors to improve the overall stability of the structure. Such comprehensive retrofit measures ensure that homes are better equipped to face the rigors of earthquake shaking, ultimately leading to a more resilient built environment.
Differentiating Between Bolt Retrofit and Brace-and-Bolt Retrofit
Bolt retrofit and brace-and-bolt retrofit are two principal methods employed to enhance earthquake resistance in existing structures. Bolt retrofit focuses on anchoring the house more securely to its foundation using bolts, thereby significantly reducing the likelihood of the structure moving independently of its base during an earthquake. This method is particularly effective for homes with a raised foundation, where there is a clear gap between the house frame and the foundation itself.
On the other hand, brace-and-bolt retrofit entails the addition of bracing to the cripple walls and bolting the house to its foundation. The bracing usually consists of wood or steel panels that are installed on the interior or exterior of the cripple wall sections to prevent lateral movement during seismic activity. When combined, bracing and bolting provide a comprehensive seismic strengthening solution, ensuring that the house is both rigid and securely anchored to its base. This type of retrofit is highly recommended for homes in seismically active regions as it addresses both vertical and horizontal forces exerted during an earthquake.
Expert Foundation Assessments for Your Peace of Mind
Our team of experienced professionals conducts thorough assessments to identify any foundation issues and provide you with detailed reports. With our expertise, you can have confidence in the condition of your home’s foundation.
Assessing the Costs: How Much Does an Earthquake Retrofit Cost?
Breaking Down the Earthquake Retrofit Cost
The cost of earthquake retrofitting a home varies widely depending on several factors, including the size of the house, the type of retrofit required, and the current condition of the building’s foundation and structure. Generally, the investment in retrofitting a home for earthquake safety can range from a few thousand dollars for basic improvements to tens of thousands for more comprehensive retrofitting work. This cost may seem significant, but it is essential to weigh it against the potential cost of earthquake damage repair, which can far exceed the initial investment in retrofitting.
Part of the retrofit cost breakdown includes expenses related to the installation of anchor bolts, the construction of cripple wall bracing, and potentially the improvement of the concrete foundation’s strength. Additionally, professional fees for engineers and contractors who specialize in seismic retrofit must be considered. While the upfront expense is notable, the peace of mind and long-term savings afforded by reducing the risk of severe damage during an earthquake are invaluable. Exploring financial assistance programs, such as those offered by governmental and private entities, can also help mitigate the cost of retrofitting.
Comparing Retrofit Costs Against Earthquake Damage Potential
The comparison between the cost of retrofitting and the potential cost of earthquake damage elucidates the economic rationale behind the decision to retrofit. While retrofitting incurs an upfront expense, the financial impact of not retrofitting can be much more substantial, particularly in the aftermath of a major earthquake. Studies have shown that the cost of repairing or rebuilding a home after a significant earthquake can far surpass the initial outlay for seismic retrofitting. Furthermore, the emotional and psychological toll of losing a home or experiencing severe property damage can be devastating and incalculable.
Moreover, the comparison extends beyond mere financial considerations. Retrofitting a home also means preserving its historical value and maintaining community continuity. Many older homes possess architectural and historical significance that would be impossible to replicate if destroyed. Retrofitting these structures ensures that they can withstand earthquakes, thus preserving a part of the community’s heritage. Additionally, homes that have been seismically retrofitted often have a higher resale value and may be more attractive to buyers who value safety and resilience in earthquake-prone areas.
Evaluating the Long-Term Savings of Retrofitting Your Home
When evaluating the viability of investing in earthquake retrofitting, long-term savings should be a key consideration. Retrofitting not only reduces the risk of significant structural damage during an earthquake but also can lead to savings on earthquake insurance premiums. Insurance companies often recognize the reduced risk profile of retrofitted homes and may offer lower rates as a result. Furthermore, the retrofit can prevent displacement costs by ensuring that the home remains habitable even after a seismic event.
Additionally, the physical and emotional well-being that comes from knowing one’s home is secure against earthquake damage is invaluable. The peace of mind associated with having taken proactive steps to protect one’s property and loved ones cannot be underestimated. While it’s difficult to quantify the exact long-term savings of retrofitting, the combined benefits of reduced repair costs, lower insurance premiums, preserved home value, and enhanced safety significantly tip the scales in favor of retrofitting. Considering these factors, the investment in earthquake retrofitting emerges as not only a wise financial decision but also a critical measure for ensuring the well-being of households in seismic zones.
Real Experiences From Real People.



The Brace and Bolt Program: A Closer Look
Understanding the Function and Benefits of the Earthquake Brace
The Earthquake Brace and Bolt program, commonly abbreviated as EBB, is an initiative designed to promote seismic safety through financial incentives for homeowners undertaking retrofit projects. The primary focus of this program is on the brace-and-bolt retrofit, a method proven to significantly enhance the earthquake resistance of homes. The earthquake brace, a component of this retrofit strategy, involves the installation of bracing materials around the cripple walls to prevent them from collapsing during seismic activity. This measure, coupled with bolting the house to its foundation, forms a robust defense against earthquake-induced forces, substantially reducing the risk of major structural damage.
Participation in the EBB program affords homeowners several compelling benefits. Not only does it provide financial assistance to offset some of the retrofitting costs, but it also offers access to a network of certified contractors skilled in earthquake retrofitting. Moreover, the program raises awareness about the importance of seismic retrofit for the overall safety of communities in earthquake-prone areas. Through the EBB program, homeowners are empowered to take proactive steps to enhance the resilience of their homes, contributing to a safer living environment for themselves and their neighbors.
How the Brace and Bolt Retrofit Works to Protect Your Home
The brace and bolt retrofit technique is a systematic approach to enhancing the structural integrity of homes to withstand the forces generated by earthquakes. This method involves the installation of metal braces to reinforce the cripple walls—short walls that enclose the crawl space under a house with a raised foundation. These braces improve the stiffness and strength of the walls, making them less prone to buckling under earthquake forces. The addition of anchor bolts ensures that the house frame is securely fastened to the concrete foundation, preventing the structure from sliding or toppling over during violent shaking.
In practice, the implementation of a brace and bolt retrofit requires thorough assessment and planning to tailor the retrofit to the specific needs of each house. Certified professionals conduct evaluations to determine the most effective placement of braces and bolts, taking into account factors such as the home’s design, age, and existing structural conditions. By adhering to established retrofit standards, these professionals ensure that the retrofit work maximizes the home’s earthquake resistance while preserving its architectural integrity. As a result, homeowners enjoy an increased sense of security, knowing their homes are more likely to withstand the destructive power of earthquakes.
Qualifying for a Brace and Bolt Retrofit Through the EBB Program
Eligibility for the Earthquake Brace and Bolt (EBB) program is determined by a set of criteria established to prioritize homes most in need of seismic retrofitting. Typically, homes built before 1980 in designated high seismic risk areas are considered prime candidates for the program, given their vulnerability to earthquake damage due to older construction standards. Homeowners interested in applying for the EBB program are encouraged to review these criteria and register for the program through its official website.
Upon qualification, participants receive guidance throughout the retrofit process, including assistance in selecting a qualified contractor from the EBB’s list of approved professionals. The financial assistance provided by the EBB program significantly reduces the out-of-pocket costs for the homeowners, making the essential retrofit work more accessible and affordable. By facilitating the retrofitting process, the EBB program plays a pivotal role in enhancing the seismic safety of communities, one home at a time. Continuous expansion and promotion of the program could lead to wider adoption of retrofit practices, ultimately contributing to a more earthquake-resilient housing stock.
Ensuring Quality: Certifications and Qualifications for Professional Retrofitting
Quality assurance in earthquake retrofitting is paramount to ensure that the retrofit work is performed to the highest standards, providing effective protection against earthquake forces. As such, it is crucial to engage contractors and engineers who possess the necessary certifications and qualifications in seismic retrofitting. Professional accreditations, such as those provided by recognized engineering associations and retrofit training programs, indicate a practitioner’s proficiency and expertise in the field of seismic strengthening.
Homeowners should conduct thorough research and vet potential contractors by reviewing their certifications, experience, and portfolio of completed retrofit projects. Engaging a certified professional not only guarantees that the retrofitting work adheres to current best practices but also provides homeowners with peace of mind, knowing their project is in capable hands. Moreover, certified professionals are more likely to be familiar with the latest advancements in retrofit technology and techniques, ensuring that homes receive the most effective seismic protection possible. As the foundation of earthquake safety, the quality of retrofit work cannot be compromised, making the selection of qualified professionals a critical step in the retrofitting process.

Securing Your Home Against Earthquake Damage: Practical Steps
Strengthening Your House’s Frame: Key Techniques in Earthquake Retrofitting
Securing the structural frame of your house is a fundamental aspect of earthquake retrofitting, focusing on enhancing the building’s capacity to bear the stresses induced by seismic activity. Key techniques in strengthening the frame include the installation of shear walls, which provide lateral support and prevent the frame from swaying, and the use of metal connectors to ensure that structural components remain firmly attached to each other during violent shaking. These measures are vital for maintaining the integrity of the house’s frame, which is essential for keeping the structure upright and protecting its occupants during an earthquake.
Additionally, reinforcing the connections between the house’s various structural elements, such as floors, walls, and the roof, plays a critical role in earthquake retrofitting. This involves the strategic placement of metal straps and anchors that tie these elements together, creating a cohesive unit that is better able to withstand the dynamic forces of an earthquake. By addressing the potential weak points within the frame, these retrofitting techniques significantly increase the home’s resilience, making it more likely to survive a major seismic event with minimal damage.
Protecting the Foundation During an Earthquake: Tips and Strategies
The foundation of a house is its bedrock, providing essential support for the entire structure. Protecting the foundation during an earthquake is of utmost importance to prevent significant damage or total collapse. Retrofitting strategies that focus on the foundation include the installation of foundation bolts, which anchor the house to its concrete foundation, and the application of cripple wall bracing, which strengthens the foundation’s perimeter and prevents it from buckling under seismic forces.
Other practical steps for protecting the foundation involve assessing and repairing any existing cracks or weaknesses. This might include the injection of epoxy into cracks to restore the foundation’s strength or the addition of new concrete to bolster its resilience. Regular inspections by qualified professionals can help identify potential vulnerabilities in the foundation, allowing for preemptive retrofitting measures that significantly enhance the house’s earthquake resistance. Taking proactive steps to secure the foundation not only safeguards the physical structure of the home but also ensures the safety of its inhabitants during an earthquake.
Minimizing Earthquake Shaking and Damage with Effective Retrofitting
Effective retrofitting techniques are key to minimizing earthquake shaking and damage. By retrofitting your home, you introduce measures designed to absorb and dissipate seismic energy, reducing the intensity of the shaking experienced inside the structure. One of the primary methods for achieving this is through the installation of base isolators, which allow the building to move independently of ground motion, thereby decreasing the transfer of seismic forces to the structure. While base isolation is more commonly applied in commercial construction, its principles can be adapted for residential retrofitting, offering a high level of protection against earthquake damage.
Another strategy involves the use of dampers, devices that absorb seismic energy and prevent it from causing structural damage. Dampers can be installed within the frame of the house, acting as shock absorbers during an earthquake. This approach, combined with the reinforcement of structural joints and the strengthening of the house’s load-bearing elements, forms a comprehensive retrofitting solution that significantly diminishes the potential for earthquake-induced damage. By implementing these advanced retrofitting techniques, homeowners can effectively safeguard their properties and ensure the well-being of their families in the event of an earthquake.
Is Earthquake Retrofitting Worth It for California Homes?
Evaluating the Necessity of Earthquake Retrofit for Homes Built Before 1980
In California, a region frequently subjected to seismic activity, the necessity of earthquake retrofitting for homes built before 1980 is particularly pronounced. These older structures often lack the earthquake-resistant design features that are standard in newer construction, placing them at greater risk during a seismic event. For homeowners, the decision to retrofit these homes is both a practical and financial consideration, balancing the cost of retrofitting against the potential for significant earthquake damage. Given the high likelihood of experiencing an earthquake in California, retrofitting not only enhances safety and peace of mind but also serves as a wise investment in the long-term durability and value of the property.
Moreover, local regulations and building codes in California increasingly recognize the importance of seismic retrofitting, with ordinances requiring the reinforcement of certain types of vulnerable buildings. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures the safety of the occupants but also protects the homeowner against potential liability in the event of earthquake-induced injuries or property damage. For homes built before 1980, undergoing a retrofit can translate into considerable improvements in structural integrity, significantly reducing the risk of foundation failure, wall collapse, or other catastrophic outcomes during an earthquake.
Comparing Earthquake Insurance Coverage vs. Retrofitting Costs
Homeowners in California must weigh the cost of earthquake insurance coverage against the expense of retrofitting. Earthquake insurance can provide financial protection in the aftermath of a quake, covering repairs or reconstruction. However, premiums are often high, and policies come with substantial deductibles, which means homeowners may still face considerable out-of-pocket expenses for damages. In contrast, investing in retrofitting may reduce the need for extensive insurance coverage, as the home’s enhanced resilience lowers the risk of major damage. Furthermore, some insurance providers offer reduced premiums for retrofitted homes, recognizing the decreased risk of severe structural damage and financial loss. Thus, from a long-term financial perspective, earthquake retrofitting presents an effective strategy for minimizing potential earthquake damage and insurance costs.
Additionally, when comparing the two, it is essential to consider the indirect benefits of retrofitting, such as the potential increase in property value and the assurance of a safer living environment. While earthquake insurance provides a financial safety net, retrofitting actively reduces the risk of damage, potentially averting the need for insurance claims. This proactive approach to earthquake preparedness can result in significant savings, both by lowering insurance premiums and by mitigating the costs associated with repairing earthquake damage. Ultimately, for many California homeowners, retrofitting emerges as a financially savvy and safety-oriented decision that offers both immediate and long-term benefits.
The Long-Term Value of Retrofitting and Seismic Upgrades in Earthquake-Prone Areas
In earthquake-prone areas, particularly in California, the long-term value of retrofitting and seismic upgrades cannot be overstated. Such investments not only enhance the structural resilience of buildings but also significantly contribute to the protection of lives and the preservation of property. The financial outlay for retrofitting is often recouped over time through a combination of reduced earthquake insurance premiums, lower risk of costly structural repairs, and increased property value. Additionally, the implementation of seismic upgrades is an essential measure for community preparedness, reducing the overall impact of earthquakes on the local infrastructure and emergency services.
The benefits of retrofitting extend beyond the immediate financial savings. Enhanced safety, peace of mind
Earthquake Retrofitting FAQs
Q: What is foundation earthquake retrofitting and why is it important in California?
A: Foundation earthquake retrofitting is a process that strengthens the connection between a house and its foundation to reduce and mitigate earthquake damage, especially important in a california earthquake prone area. Given the history of damaging earthquakes like the 1989 Loma Prieta and the 1994 Northridge earthquakes, retrofitting can prevent your home from sliding or collapsing during an earthquake, making it an essential precaution in earthquake country.
Q: How can foundation bolting help protect my home during a California earthquake?
A: Foundation bolting involves attaching your house directly to the foundation with strong bolts, which is a key retrofit technique. This prevents the house from sliding off its base in the event of a California earthquake, directly addressing vulnerabilities by strengthening your house against seismic forces. It is particularly effective for older houses in the bay area built before modern seismic codes were established.
Q: What is a cripple wall and how does it relate to earthquake retrofitting?
A: A cripple wall is the short wall that exists between the foundation of your home and the first floor, commonly found in older houses with a space under the house. This wall is vulnerable to earthquake damage, as it can collapse when shaken. Seismic retrofitting often includes reinforcing cripple walls with plywood to make them more sturdy and resistant to the forces of an earthquake, hence less likely to collapse.
Q: Does my home in the San Francisco Bay Area qualify for an EBB retrofit program?
A: If your home is in the San Francisco Bay Area, you might be in earthquake country and could qualify for an Earthquake Brace and Bolt (EBB) retrofit program. This program offers seismic retrofit grants to homeowners, focusing on houses built before seismic standards were updated. Qualification generally depends on the age of your home, its structural characteristics, and its location in relation to seismic hazard zones.
Q: How long does it take to complete the retrofit of a house vulnerable to earthquake damage?
A: The time required to complete the retrofit of a house vulnerable to earthquake damage can vary greatly depending on the size of the house, the specific retrofitting actions needed, and the complexity of the work. Generally, a basic retrofit can be completed in a few days to a few weeks. However, more extensive retrofits that require significant structural modifications might take longer to complete.
Q: Is retrofitting worth it in the Bay Area given the cost?
A: Absolutely, retrofitting is worth it in the Bay Area. The cost of retrofitting may seem high initially, but it is an investment in your property’s safety and can significantly reduce the risk of major damage in a devastating earthquake. Additionally, retrofitting can lower insurance premiums, increase property value, and provide peace of mind. Retrofit costs vary, but seismic retrofit grants and incentives are available to help offset expenses.
Q: How does foundation retrofitting mitigate earthquake damage to older houses?
A: Foundation retrofitting mitigates earthquake damage to older houses by addressing structural weaknesses. Methods like foundation bolting, installing plywood on cripple walls, and anchoring the floor system directly to the foundation can significantly strengthen an older house, making it more resistant to the lateral (side-to-side) forces experienced during an earthquake. This can prevent the house from detaching from its foundation or collapsing – common vulnerabilities in houses not built to current earthquake standards.
Q: How much does it generally cost more to retrofit an older house in the Bay Area?
A: The cost to retrofit an older house in the Bay Area can vary widely based on the size of the home, the scope of work required, and local labor rates. Generally, costs can range from a few thousand dollars for basic retrofits to tens of thousands for more comprehensive upgrades. It’s important to get a detailed inspection and quote from a qualified retrofitting professional to understand the specific needs and costs for your home.